Urban Greening Design, Green walls, Pollutant Dispersion, Deposition, CFD Simulation
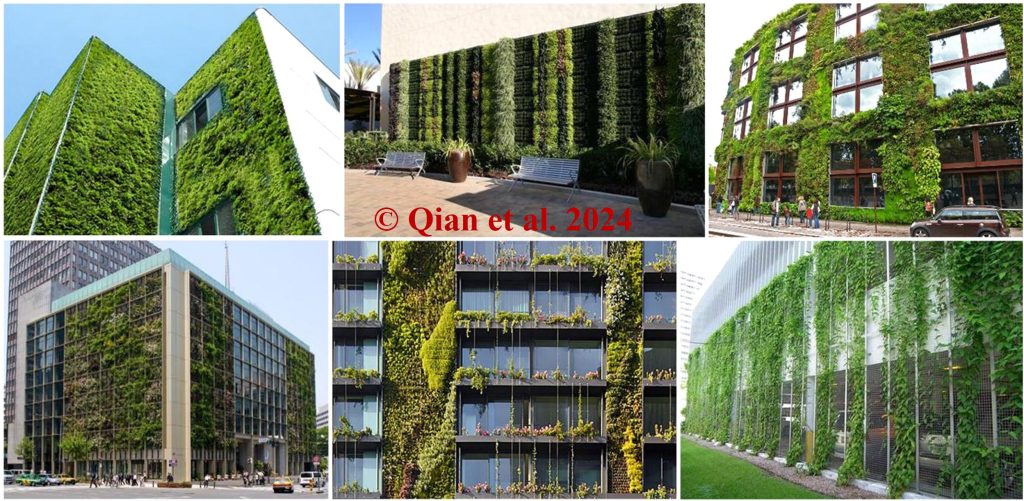

Green walls can effectively filter particulate pollution through deposition processes. Green walls provide design flexibility in planting schemes, vegetation types, and wall coverage rates.
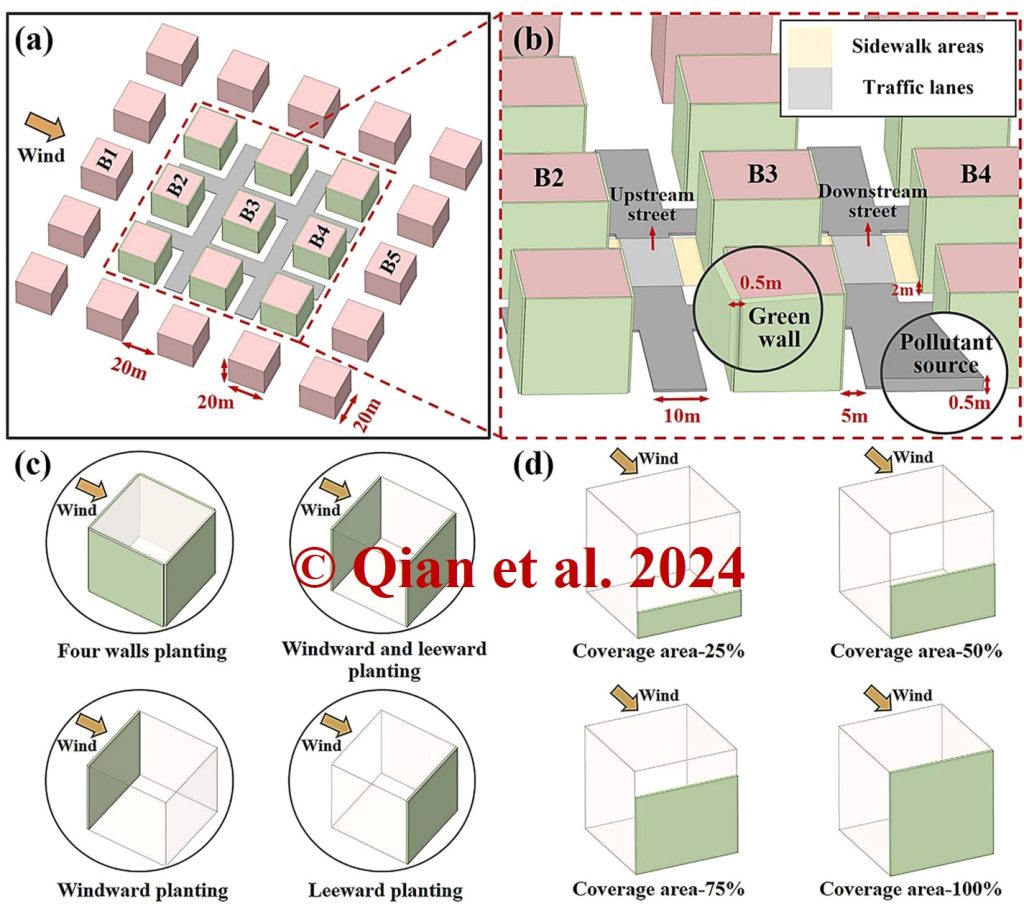
Research scenarios on mitigation effects of fine particulate pollution by applying green walls, with integrative consideration of the aerodynamic and deposition effects of vegetation.
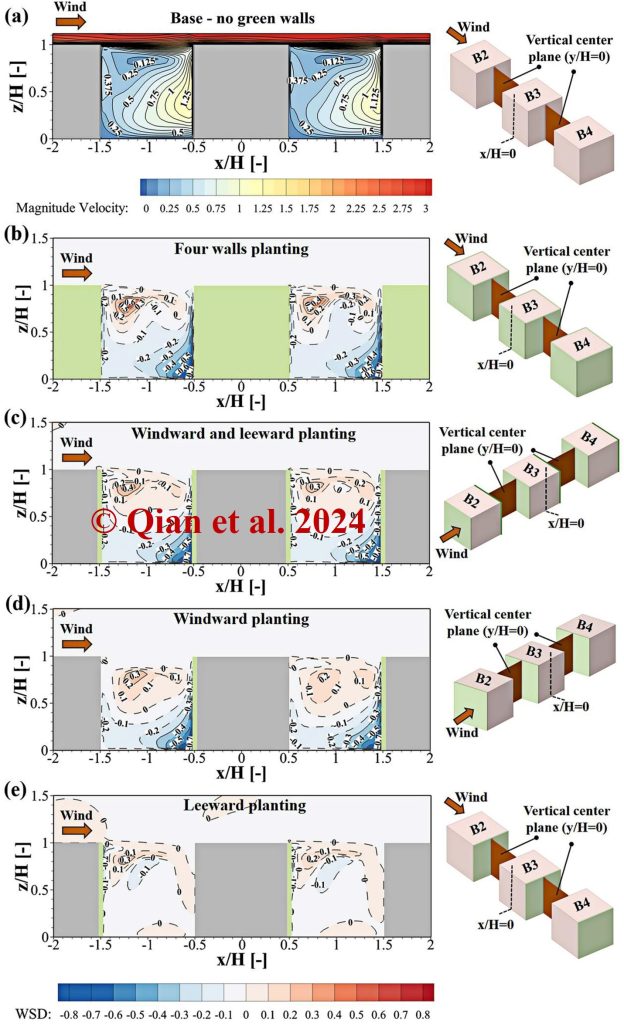
WSD distribution for the four planting strategies, indicating the local wind speed variations. In terms of ventilation, leeward planting is the most efficient.
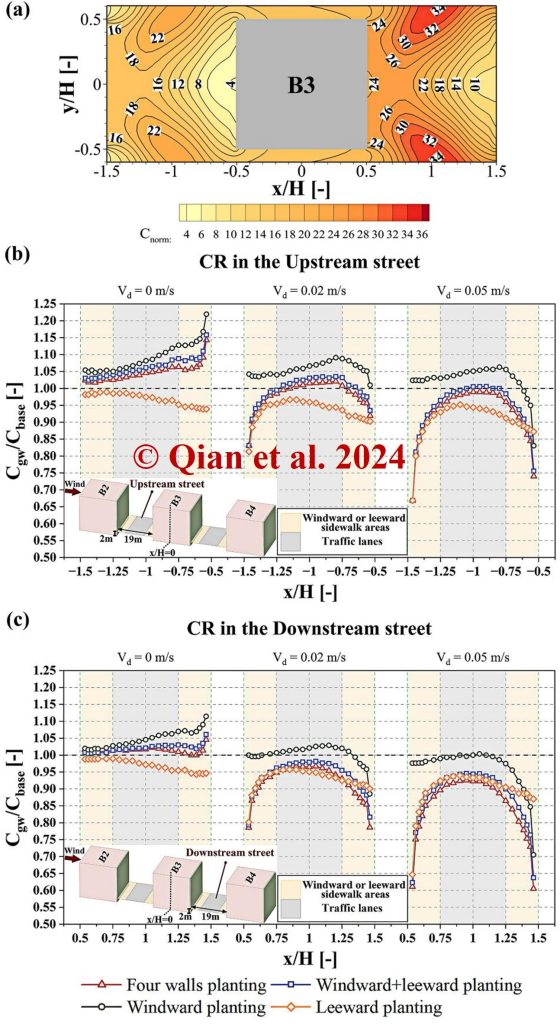
Leeward planting emerges as the preferred strategy, efficiently reducing pollution concentrations on both windward and leeward sides of streets. Pollution mitigation effect is enhanced with increasing VD and LAD values.
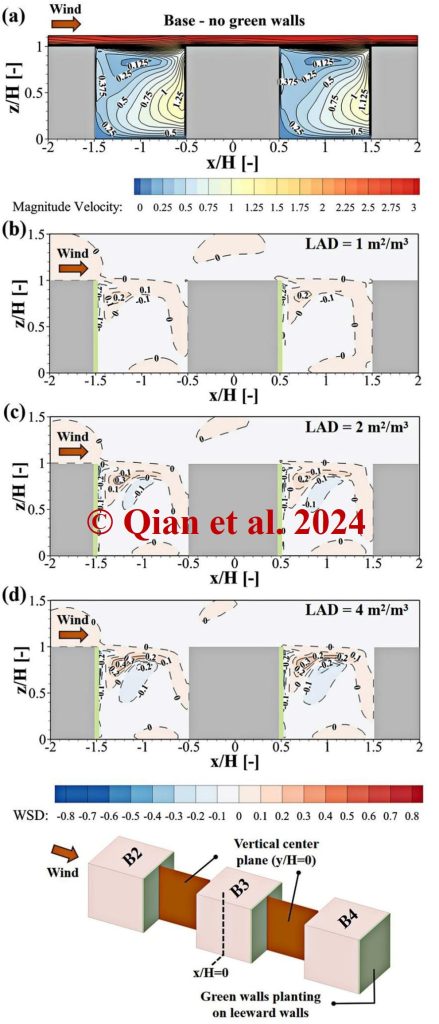
The variations in wind speeds become more pronounced as the LAD increases, due to enhanced aerodynamic effects. The coupling effects of the urban wind field and vegetation influence ventilation patterns in built-up areas and street canyons.
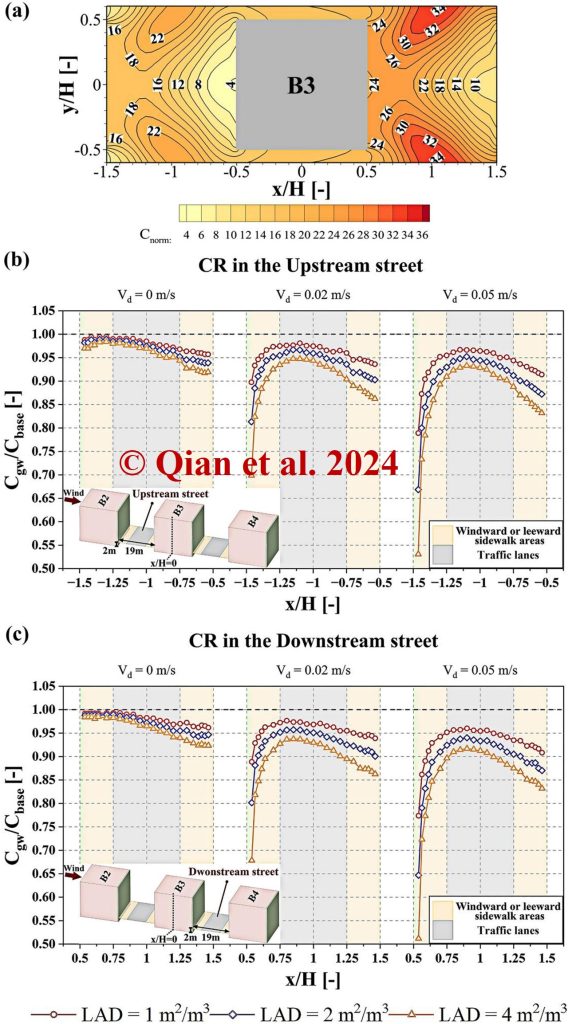
All LAD and Vd values result in CR below 1, indicating reduced pollutant concentrations at pedestrian levels.
Pollution mitigation efficiency improves with increasing LAD and Vd, with larger LAD enhancing efficient pollutant removal for all Vd values.
LAD = 4 m²/m³ and Vd = 0.05 m/s achieve the highest pollution mitigation efficiency.